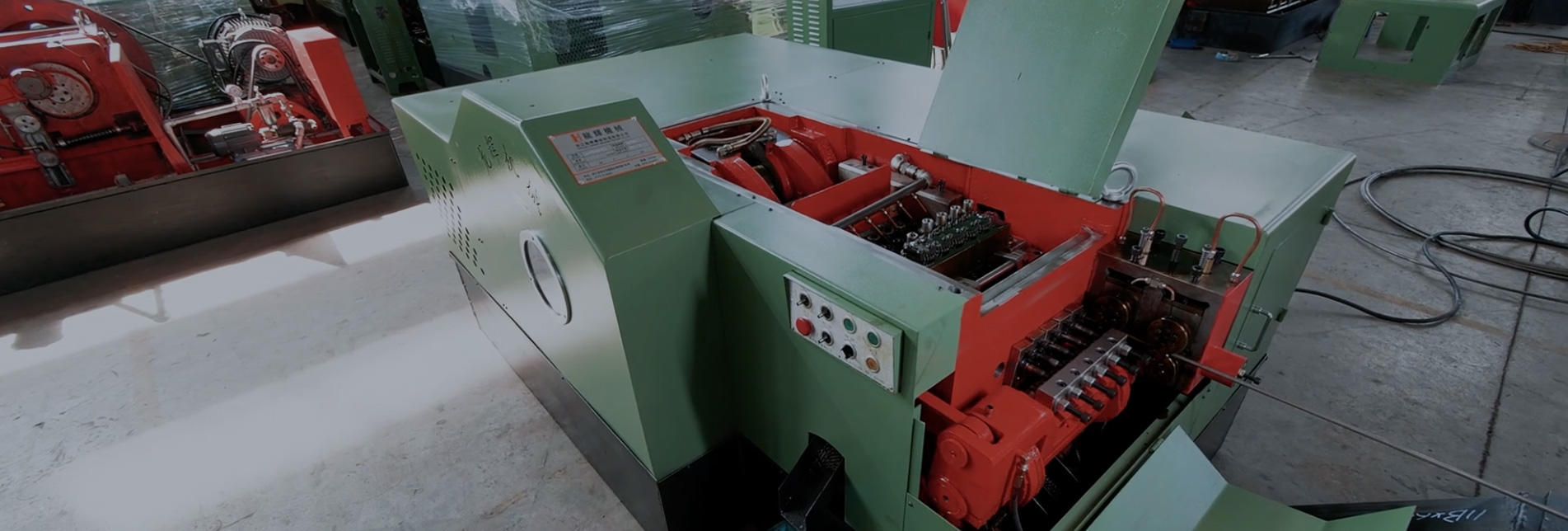
Understanding Heading Machines
Heading machines, also known as header machines, are specialized tools designed for the precise shaping and forming of components, typically from metal or wire stock. These machines are known for their versatility and are used in various manufacturing processes, enabling the production of components such as fasteners, screws, bolts, and more. They can shape materials at room temperature, which distinguishes them from hot forging methods.
The Working Process
The operation of a heading machine involves several key steps:
Feed and Cutoff: The process begins with a continuous feed of wire or rod material into the machine. The machine's cutoff mechanism accurately portions the material, creating blanks for the heading process.
Heading: In this crucial step, the machine clamps the blank, holding it securely, while the header tool shapes it into the desired form through the application of significant force. The material undergoes plastic deformation, allowing it to assume the shape defined by the die.
Trimming and Piercing: Depending on the specific requirements of the component, the machine may perform trimming or piercing operations to achieve the final design.
Ejection: Once the heading process is complete, the finished component is ejected from the machine, and the cycle begins anew.
Applications of Heading Machines
Heading machines have versatile applications across numerous industries. Some notable applications include:
Automotive Industry: These machines play a pivotal role in the production of automotive fasteners, such as bolts, screws, and rivets, ensuring that the components meet the stringent quality and safety standards of the automotive sector.
Construction: Manufacturers in the construction industry rely on heading machines to produce high-strength fasteners and connectors for structural components.
Aerospace: In the aerospace sector, heading machines are employed to create specialized fasteners and components used in aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft, where precision and reliability are paramount.
Consumer Goods: These machines are utilized for creating a variety of consumer products like furniture hardware, toys, and sports equipment.
Electronics: The electronics industry benefits from the precision of these machines to craft connectors, terminals, and fasteners used in electronic devices and circuitry.
Medical Devices: The medical sector leverages the precision of these machines to manufacture components used in medical instruments and equipment, where quality and sterility are critical.
Advantages of Heading Machines
Heading machines offer numerous advantages that significantly enhance manufacturing efficiency:
Precision: These machines enable the production of components with precise dimensions and tolerances, ensuring high-quality products that meet stringent specifications.
Material Savings: The heading process minimizes material waste, contributing to cost savings and resource efficiency.
High Production Rates: Heading machines can operate at high speeds, making them ideal for large-scale production.
Strength and Durability: Components produced by these machines are known for their superior strength and durability, making them suitable for critical applications that demand reliability and performance.
Consistency: The process ensures consistent and uniform results across all components, reducing the likelihood of variations in product quality.
Challenges and Considerations
While heading machines offer numerous benefits, they also present specific challenges and considerations:
Tooling and Die Maintenance: Proper maintenance of the machine's dies is crucial to maintaining the quality and precision of the components. Regular inspection and refurbishment are necessary to avoid defects and ensure consistent results.
Material Selection: The choice of the appropriate material is essential to achieving the desired results, as certain materials are better suited for the heading process.
Secondary Operations: Depending on the component's design, secondary machining or additional operations may be required to meet specific requirements.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى

